Occasionally, Office 365 users will delete important mailbox items accidentally. Fortunately, in most cases such items can be recovered for a short period of time after their deletion. In this article we will discuss what happens when mailbox items are deleted and the circumstances required to successfully recover them.
What happens when mailbox items are deleted?
When Office 365 end users soft-delete (Ctrl+D) an item from their mailbox, it goes to the Deleted Items folder from which it can returned to the original location very easily. This procedure is simple as the end user has direct access to the Deleted Items folder.

The items stay in the Deleted Items folder until they are automatically cleared or removed by the end user. In earlier Office 365 versions, soft-deleted items remained in the Deleted Items folder for 30 days. Now they remain there for period of time determined by the Office 365 (Exchange Online) administrator. This duration can be changed by updating the Messaging Records Management (MRM) policy.
How to update the MRM policy
Administrators can create a new MRM policy by editing the default one from the Exchange admin center. To edit the Default MRM policy, go to compliance management > retention policies, select the Default MRM Policy, and click the edit icon. Change the policy name, set the retention time and click Save.

Permanent deletion of items
An item is permanently deleted if any of the following occurs:
- The end user deletes it from the Deleted Items folder
- The end of the retention period is reached
- The end user hard-deletes (Shift + Delete) the item from any folder

Permanently deleted items go to the Deletions folder (inside the invisible Recoverable Items folder of the mailbox). Whilst the end user has no direct access to this folder, the items can still be recovered for a short period after their deletion.
How to recover permanently deleted items
To recover permanently deleted items, click Recover Deleted Items (in the Folder ribbon) in Outlook. A new window with the list of all the recoverable items appears. Select the required items and click Restore Selected Items. When recovered, the items go back to their original location.
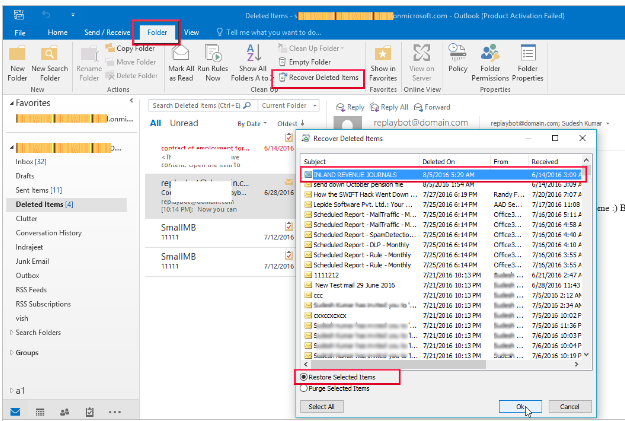
By default, the permanently deleted items stay in the Deletions folder for 14 days, and are recoverable for this period. Office 365 administrators can increase this duration to 30 days if they wish to do so.
For detailed information on changing the retention period for an Exchange Online mailbox, see the links in the resources section at the end.
Can the deleted items be recovered from on-premises Exchange?
Deleted items from user mailboxes can be recovered using the inbuilt features of on-premises versions of Exchange. However, the process is slightly time-consuming and there are much easier ways to go about it. One such way is to deploying a specialized third-party recover solution, Like Lepide Exchange Recovery Manager. This solution displays the deleted items on the preview pane, highlighting them in red, and can be used to recover deleted items from multiple user mailboxes at once.
Conclusion
Soft-deleted Outlook items can be recovered easily from the ‘Deleted Items’ folder by the users themselves. Exchange Online administrators can also update the Office 365 MRM policy to ensure the items stay in the ‘Deleted Items’ folder for longer periods. However, when items enter a permanently deleted state, the recovery, while still possible, becomes a much more laborious task as end users cannot simply do it themselves. In cases like this, deploying solutions like Lepide Exchange Recovery Manager can help save IT teams time make life easier for end users.
Resources:
For detailed information on changing the retention period for an Exchange Online mailbox, refer to the Microsoft TechNet article: https://technet.microsoft.com/library/dn163584(v=exchg.160).aspx
Anything I delete does not go into the delete file